
MS Access
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional Resources
MS Access XP |
 |
Beginning with a brief explanation of databases in general, this page gives you a quick look at opening, saving and closing an Access database.
 |
What's on this page... Starting Access Parts of the screen Understanding Access toolbars Exiting Access |
Starting MS Access
You can start MS Access in several ways, depending on how you’ve installed it. One way is to use the Start menu button.To start Access, follow these steps:
| 1. | Click the Start button. A menu appears. |
| 2. | Select Programs. A list of your program groups appears, with a list of separate Microsoft applications under the groups. |
| 3. | Click Microsoft Access in the list of applications. Access starts. |
Parts of the Screen
Access is much like any other Windows program: It contains menus, toolbars, a status bar, and so on.Notice that in the following picture, many of the toolbar buttons are grayed out (which means you can't use them right now).
In addition, nothing is in the work area because no database file is open. The Access screen becomes a much busier place later on. You'll notice that when you begin working with a database, the buttons become available, and your database appears in the work area.
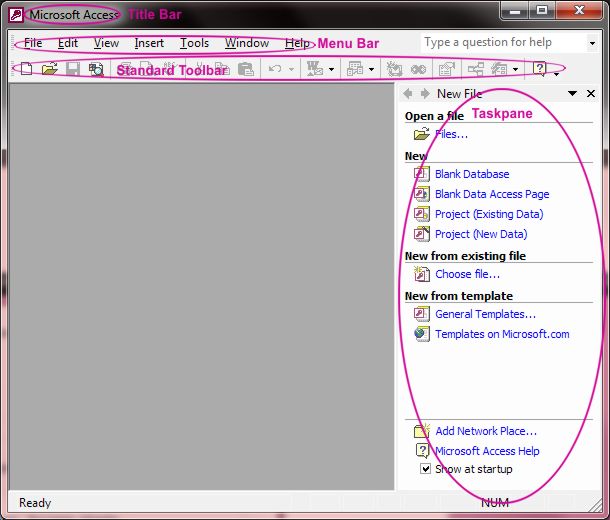 |
Understanding Access Toolbars
If you've used Windows programs before, you're probably familiar with toolbars — rows of buttons that represent common commands you can issue.The MS Access toolbar changes, depending on which type of database object you're working with at the time (tables, forms, reports, queries, and so on) and what you're doing to it. More toolbars sometimes appear when you're doing special activities, such as drawing.
To find out what a toolbar button does, put your mouse pointer over it; a name appears underneath the pointer. This feature is called a ToolTip (or a ScreenTip); you can use ToolTips even when a button is unavailable (grayed out/dimmed).
 |
Choose Your Toolbars If you right-click any toolbar, a shortcut menu appears. You can select a toolbar for viewing from that list. You can also use the View ► Toolbars command, to select the toolbar you want. |
Exiting Access
When you finish working with Access, you should exit it to free up your computer's memory for other tasks.You can exit Access in several ways:
| ► | Press Alt + F4. |
| ► | Choose File ► Exit from the menu bar. |
| ► | Click the Access window’s Close (X) button in the upper-right corner of the window. |
Access saves all the data automatically. You won't find Access asking you to save the changes unless it's very necessary.
| Back to Top |
| Return to Microsoft Access Help from MS Access |
Access XP Topics
- Screen layout- Toolbars
- Storing data
- Database planning
- Tips for tables
- Tips for forms
- Tips for reports